The Melasma Clinic
AT SHINE MD
Melasma is a common skin condition that presents as patches of dark pigmentation on the skin. Melasma most commonly affects the forehead, upper lip and cheeks.
Often referred to as the “mask of pregnancy,” melasma frequently affects pregnant women and can fade after childbirth. For those who experience chronic melasma, the condition usually darkens and lightens with time, becoming most visible in the summer months or with increase in sun exposure. Though melasma is not painful or physically uncomfortable, people who are affected by melasma have a significant impact on their quality of life.
Book a melasma consultation at our Vancouver clinic.
Mixed Hyperpigmentation describes a clinical scenario where there are a few causes of pigmentation and one of those could be melasma. Other forms of pigmentation that can be difficult to differentiate from melasma are sun spots and sun related hyper pigmentation. Post inflammatory hyperpigmentation from acne or inflammation of the skin (dermatitis) can also be tricky to separate from a melasma diagnosis.
Dr. Khurana and the Team at Shine MD have made a strong commitment to treating pigmentary conditions and improving access to care for skin conditions that are often overlooked. Melasma is a chronic condition that does not resolve completely. Therefore it can be a difficult journey for the patient.
What Causes Melasma?
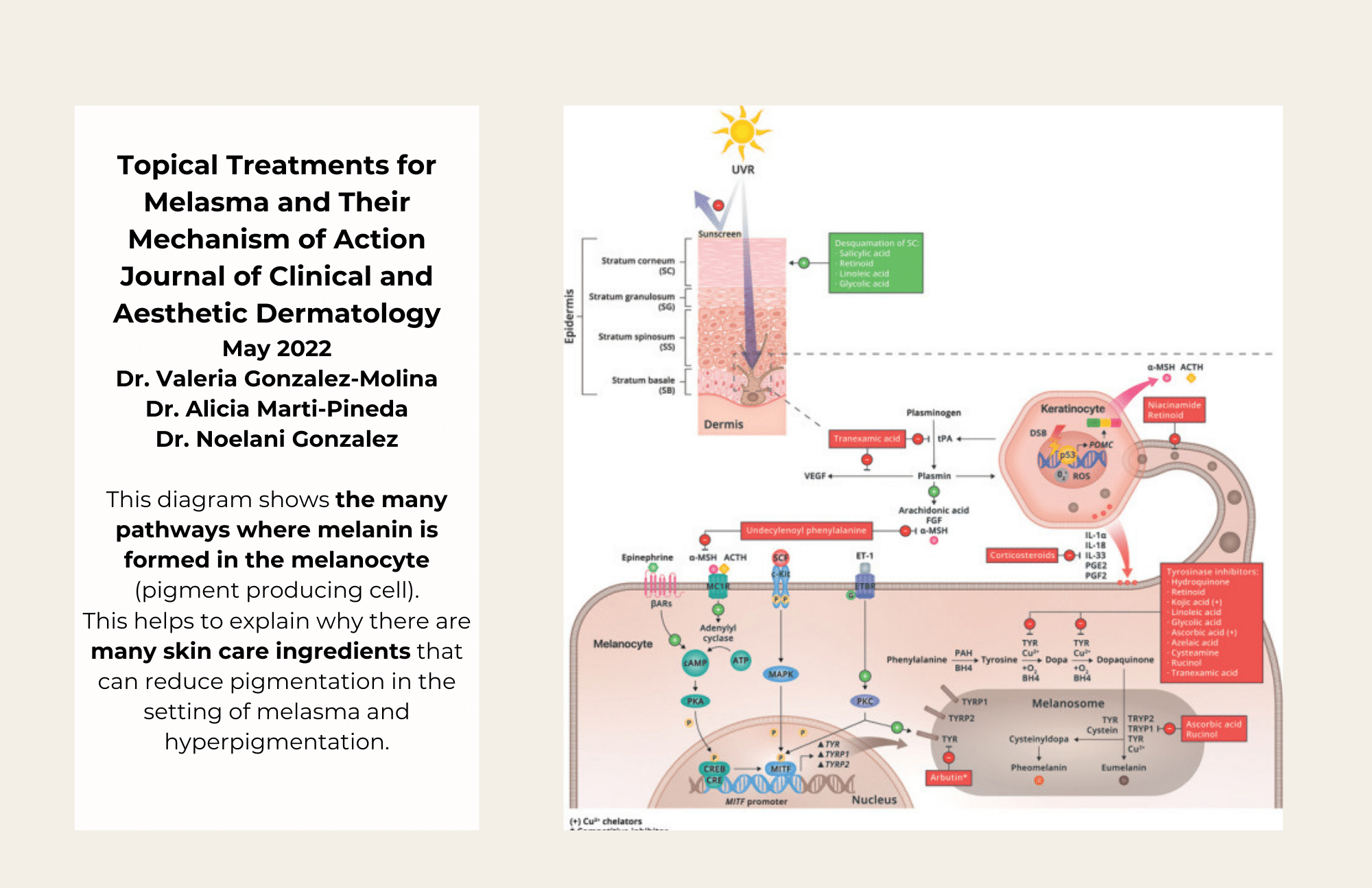
As you may know, the pigment that gives our skin its tanned color is called melanin. Melanin is responsible for our skin tones, eye colors, and hair colors, and it protects us from the harmful UV rays emitted by the sun. Specialized skin cells called melanocytes are responsible for producing and storing melanin. When we experience sun exposure, melanocytes generate more melanin to protect us, darkening our skin.
Melasma occurs when melanocytes overproduce melanin, and pigmented patches appear on the skin. The melanocytes become overactive and do not have a normal “off switch”. People of color are more likely to experience melasma, as darker skin has more active melanocytes than lighter skin. Up to 40% of South Asian females can be affected by melasma. There is also a genetic predisposition for melasma. Women are also significantly more likely to have melasma than men, and according to the Cleveland Clinic, 90% of melasma cases affect women. Scientists believe this may be because female hormones contribute to the development of melasma. Pregnant women are at risk for experiencing melasma, and women who take hormonal birth control or other medications containing synthetic estrogen are also more at risk. After pregnancy, melasma often fades away but may remain present, creating a challenge in the postpartum time.
Melasma triggers include hormones (birth control pill, pregnancy), sun exposure, light, heat and genetics, Heat, light, and UV rays are a key component to worsening melasma. Research has shown that melasma can also be worsened by the ultraviolet rays produced by tanning beds, or even by frequent exposure to LED lights emitted by screens.
Melasma Treatment at Shine MD
Mission Statement:
To advocate for patients with melasma and mixed hyperpigmentation and offer treatment options that:
- Provide evidence based treatment to improve melasma and pigmentation.
- Create treatment plans to minimize aggravation of pigmentation.
- Provide ongoing support and education to help improve quality of life in melasma patients.
Melasma may look similar to other skin pigmentation, like sunspots or freckles. It can be mistaken for other skin conditions. The team at Shine MD will assess your skin to determine if you have melasma. Sometimes, if many forms of pigmentation are visible or the melasma is slight, it can be challenging to determine the presence or extent of melasma.
The key issue in this situation is choosing the right treatment or laser to treat your pigmentation. In the case where melasma is a clear diagnosis or there are many forms of pigmentation present (mixed hyperpigmentation) and melasma is a likely component, extra care needs to be taken in treating your pigmentation.
The Melasma Clinic at Shine MD has been established as a part of our deep commitment to treating pigmentary conditions and conditions that commonly affect patients with skin of color.
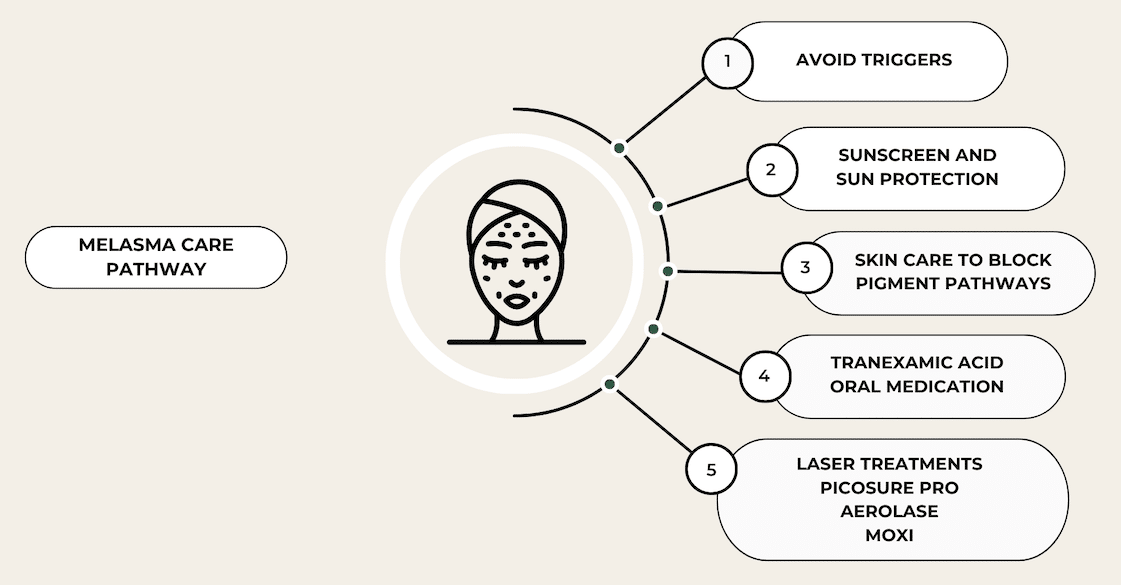
Key Steps to Melasma Treatment
The treatment of melasma is a multifaceted process.
Avoid Triggers: Avoid sun exposure by wearing a wide brimmed hat and gravite towards the shade. Avoid chronic unprotected sun exposure in your younger years. Exposure to hormones in the form of oral contraceptives can worsen your condition. For some patients, heat can aggravate melasma.
Wear Sunscreen: Sunscreen is one of the most important interventions in minimizing your melasma. If possible, choose a tinted sunscreen that helps to block out visible light in addition to UVA and UVB light. Apply at least two finger breadths of sunscreen (two finger rule). Reapply your sunscreen every two hours. If you do not want to reapply sunscreen, buy a powdered sunscreen that will not interfere with your makeup when being reapplied throughout the day.
Skin Care Program: Commit to a skin care regimen that helps to block pigment pathways that produce melanin. Tinted sunscreen protects against UV and visible light. Skin care ingredients that contain hydroquinone, cysteamine, arbutin, kojic acid and retinol (among others) block the pigment producing pathways in your skin. Retinols improve turnover of the outermost layer of the skin. This helps to improve clearance of pigment and allow deeper absorption of other ingredients. Vitamin C acts as a pigment pathway blocker and as a powerful antioxidant. Cysteamine (Sente) is a new product and is research proven to be equally as effective as hydroquinone. There is no limit on the duration of use. It will not cause darkening of the skin.
Tranexamic Acid: You may be a candidate for an oral medication that decreases the inflammatory and vascular pathways that worsen melasma. Traditionally, tranexamic acid has been used in medicine to decrease bleeding in trauma victims or to help improve heavy periods. For treatment of melasma, tranexamic acid is given at a fraction of the dose and helps to slow down the inflammatory pathways that contribute to melasma. The majority of patients will see an improvement in pigmentation within two months of taking the medication. Because TXA increases the clotting capacity of your blood at certain doses, it has the possibility of increasing your chance of having a blood clot in your leg or lungs. In melasma, the dose of TXA is so low that research has shown it is very unlikely to cause blood clots. However, you are unable to take this medication if you have a history of blood clots in your legs or lungs or if you have a family history or genetic predisposition to forming blood clots.
PicoSure Pro Laser: This technology is leading the way in offering a safe and reliable approach to treating pigmentation and also helps stimulate collagen production at certain settings. The PicoSure Pro Laser is the only device that has been officially FDA approved for the treatment of melasma. The treatment beam has a high affinity for melanin and essentially shatters the pigment, making way for your body’s natural mechanisms to clear up the pigment over time. This uses a fast picosecond beam and does not apply heat to the tissue. Therefore, it does not aggravate the melanin producing cells to cause rebound pigmentation. Treatments are done in a series of three, one month apart and must be coupled with sun avoidance and sun protection, sunscreen and appropriate skin care. Treatment plans are likely to require more than three sessions and require a low and slow approach to gently reducing pigmentation. Treatments have low downtime, with one to two days of redness and no disruption of the skin barrier. This can be performed all year round and on all skin types. Darker skin types are likely to require a test patch.
What other treatments are safe for patients with melasma?
Patients with melasma often have other skin care goals of improving texture, acne scarring or redness.
For melasma patients with rosacea, the Neo Elite by Aerolase is a good option to remove redness and small vessels. For melasma patients with acne the Neo Clear is a safe option for reducing acne, redness and pigmentation.
Acne scarring, fine lines and wrinkles can be treated with Potenza or Morpheus8 radiofrequency microneedling. SkinPen Microneedling with PRP or Tranexamic Acid topical solution are also safe and have the lowest risk of triggering or worsening melasma.
Injectables, Dermal Fillers and Sculptra are all safe and do not trigger or aggravate melasma.
Your medical assessment for melasma may be covered by the Medical Services Plan of British Columbia with an MSP referral.
It is important to note that melasma is a challenging condition to treat. There is no single cure for melasma. The goal of treating melasma is to minimize your pigmentation and improve your quality of life. Treatments are aimed at reducing pigmentation. The use of lasers in the treatment of melasma is performed frequently, with thoughtful consideration of patient goals and expectations.
We offer the following treatments that can help improve the appearance of melasma: